Data analytics is the process of exploring, transforming, and examining data to identify trends and patterns that reveal important insights and increase efficiency to support decision making. A modern data analytics strategy enables systems and organizations to work from automated, real-time analytics, ensuring immediate, high-impact results.
The data analysis process
The data analysis process is based on several steps and phases. Conclusions from later phases may require rework at an earlier phase, which is more of a cyclical process than a linear one. Most importantly, the success of data analysis processes depends on the repeatability and automation of each of these steps.
The analysis process is best divided into the following steps and phases:
Data entry: determines the requirements and collects the data. This involves a bit of investigative work, such as talking to stakeholders, finding out who is responsible for the data, and gaining access to the data.
Data Preparation: This is the strategy and tactics of preparing data for its primary goal of producing analytics insights. This includes cleaning and consolidating raw data into well-structured, analytics-ready data. It also includes checking the results at each part of the preparation process to make sure the analysis is producing the desired results.
Data exploration: Data exploration, or exploratory data analysis, is the process of studying and investigating a large set of data through sampling, statistical analysis, pattern identification, and visual profiling, among others. The methods are not necessarily scientific or conclusive, but serve to better understand the transformation of the data.
Data Enrichment: Data is enriched and augmented with additional inputs and data sets to enhance analysis. This step in the data analysis process is critical to revealing new insights by looking at data from a new perspective.
Data science: It is about applying more advanced methods of data mining to obtain deeper and more difficult to extract meanings and insights, which are largely unattainable through more rudimentary modalities of data processing. This includes algorithms, model training, machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI), to name a few.
Business intelligence: Business results can be achieved through the combination of an organization’s data, software, infrastructure, business processes, and human intuition. The results deliver actionable insights through reports, dashboards, and visualizations to help drive business decisions.
Reporter: The results of data analysis must be shared in an effective way that preserves the insights gained. Report Builder organizes that knowledge and its results in an easy-to-understand format.
Optimization: Because variables change over time, models need to be optimized and improved to continue to serve their original purpose or to evolve from this purpose based on new inputs or changing features.
Types of data analysis
There are several different types of data analysis. These are the following:
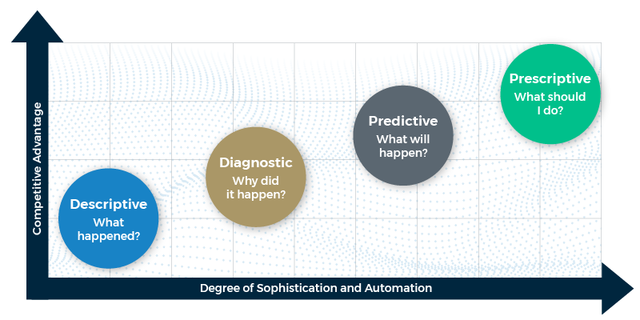
- Descriptive analysis: answers the question “What happened?” (What were our sales last week?)
- Diagnostic Analysis – Answers the question “Why did this happen?” (Why did our sales increase from the previous week?)
- Predictive analytics: answer the question “What will happen?” (How do we think our sales will be in those same stores during the holiday season?)
- Prescriptive Analytics: Answers the question “What should I do?” (Based on our predictions, we recommend shipping more of a given product to avoid stockouts.)
Descriptive and diagnostic analytics allow data analysts and leaders to level the whole. These processes are building blocks that pave the way for more sophisticated insights from predictive and prescriptive analytics.
Creation of a consolidated data analysis base
The data is in any system or organization that currently exists. Many systems or organizations use analytics to improve their processes or obtain impactful results. There is no doubt that data analysis is important. The focus of modern organizations is to establish a consolidated data analytics strategy, ensuring real-time insights and forward-looking decision making.
A modern analytics solution depends on automation
Within the data analytics practice there are a plethora of point solutions that fit each step or phase mentioned above in the data analytics process. However, a major problem with the point solution approach is the inability to easily automate the entire data science and analytics process. Analysis automation enables true real-time analysis, as it is based on the automation of the entire process in a single analytical solution .
With the introduction of data analytics automation, organizations and analytics teams can automate each and every part of their analytics process—from initial data entry, cleaning, enrichment, data science, and machine learning, to writing data to relevant applications, cloud databases, BI platforms, etc.), all included in a single solution.
A modern organization depends on an Analytics Center of Excellence
Additionally, a company’s ability to compete in the emerging digital economy requires faster, more forward-looking decisions. Therefore, modern systems and organizations looking to digitally transform should consider a modern data analytics strategy as a “key accelerator” of their initiatives.
Creation of a Data Analysis Center of Excellence
A center of excellence is a centralized analytics function, developed to effectively spread and implement a culture of data analytics as a priority throughout the organization, with the goal of improving operational efficiency and processes. This results in dramatic improvement in decision making throughout the organization and real-time business results. With an effective center of excellence, organizations have internal training, consulting, guidance, and support, can drive best practices, implement an analytics modeling framework, and maximize return on investment.
A successful center of excellence will also be the means to connect data, analytics, processes, and people. The convergence of these four pillars ensures the democratization of data across the organization, empowers analysts to become citizen data scientists, automates the analytics process throughout the analytics pipeline, and facilitates employee training.
Data Supports Investment in a Strong Center of Excellence: A recent survey cites the driving effect of a common, enterprise-wide set of tools and methods for accessing and analyzing data. This survey specifies that of the 26% of companies that are doing this well, 80% exceeded their business objectives. And of companies where all staff were trained on how to use data, 88% exceeded their goals compared to 61% of those that only trained some employees.
Modern Data Analytics Case Studies
The use cases for data analytics in a digital-first world are nearly endless, from predicting customer behavior from omnichannel interactions to anticipating changes in a supply chain due to natural disasters. Let’s analyze some of the most common examples that occur in all sectors.
Supply chain
- Driving Efficiency Through Reporting: Alteryx + Daimler Trucks North America
- Safety Stock Optimization – Customer Video – Amway
- Omni-Channel Logistics : Seko Omni-Channel Logistics
CPG/Retail
- Promotional Insights: 7-Eleven
- Customer Sentiment Prediction: Mayborn
- Product Placement AB Testing: Barnes & Noble
Health
- Medical research on COVID-19 to save lives: Castor + The Information Lab, The Netherlands
- Risk Mitigation: Kaiser Permanente
- Self-Service Membership and Claims Processing: Blue Cross Blue Shield North Carolina (BCBS NC)
Public sector
- Critical situations of demand and resources: Integratis
- Predicting the Extent of Structural Damage: FEMA
- Contact tracing: Infobrief of the public sector
Financial services
- Global Financial Crime Compliance: MUFG Bank
- Centralized analysis strategy: UBS
- Personalized Tax Advice: Brookson
Finance Office
- Reducing Fraud, Waste and Abuse: Aprio
- Automation of accounting, tax and financial processes: Capitalize
- Improving Accuracy of Complicated Entity Structures – On- Demand Webinar